
Are you looking for more stability within your business? Would you like to have predictable income? Then understanding recurring revenue is essential to reach your goals. In this blog, we'll explore what recurring revenue means, examples of recurring revenue models and their benefits and challenges so that you can leverage it effectively.
What’s in this article?
So, what exactly is recurring revenue? It refers to the predictable income a business generates at regular intervals from ongoing subscriptions, contracts or memberships. Unlike one-time sales, recurring payments ensure consistent cash flow, fostering long-term financial stability. It's the essence of subscription-based businesses and an increasingly vital component across multiple industries.
To expand on the definition, let’s take a look at some of the most popular types of recurring revenue: subscription-based model, Saas and membership. Take a look at the examples of recurring revenue models to see which is the most suitable for your business.
Customers pay a regular fee for access to a product or service, such as software, streaming platforms or meal delivery services. Two well-known examples include Netflix and Hello Fresh. Subscription-based models have seen a huge increase over the last few years since Covid-19, with consumers and merchants adapting to the change in the market and payment preferences.
Users subscribe to cloud-based software on a monthly or yearly basis, accessing updates and support throughout their subscription. SaaS subscriptions are widely used within work environments, such as Microsoft 365 and Salesforce.
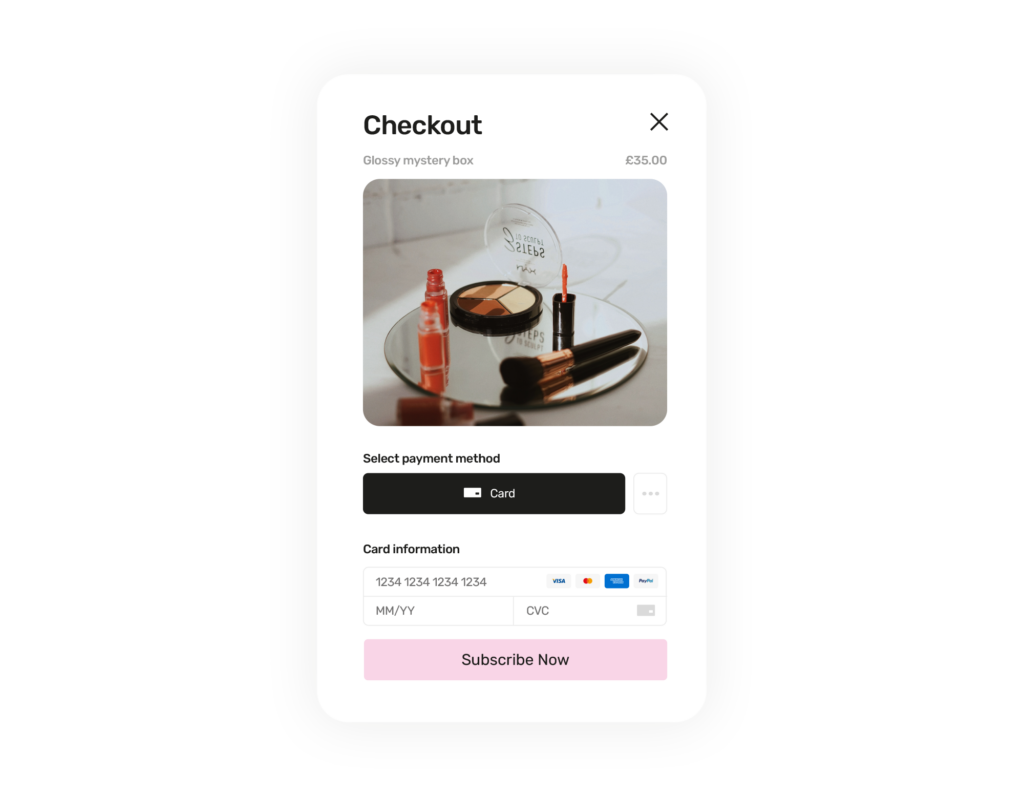
Memberships can be more than just paying for a service; it can be a community. Customers pay a recurring fee for special perks or exclusive content or access, commonly seen in gyms, online courses or premium content platforms. It's all about feeling valued and connected, and every time a customer renews, it shows they're happy with what they're getting.
There are many advantages of recurring revenue. Let’s take a look at the ones that will benefit your business the most:
Like anything to do with business and payments, recurring revenue can come with its challenges too:
What’s the difference between monthly recurring revenue and annual recurring revenue?
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) represents the predictable monthly income from subscriptions, while annual recurring revenue (ARR) reflects the total annual income from subscriptions, often calculated by multiplying MRR by 12. To go into detail, check out our blog on how recurring revenue can grow your business.
How can I track my recurring revenue?
You can track your recurring revenue effectively by:
Recurring revenue is an essential pillar of sustainable business growth. By embracing recurring revenue models, merchants can reap the benefits from enhanced cash flow to improved customer loyalty. However, navigating the complexities of recurring revenue requires diligence, adaptability and a customer-centric approach. By implementing best practices, businesses can thrive in an increasingly subscription-driven economy.
But now you know what it is and the benefits of recurring revenue, next up, let’s work out if a subscription-based model is right for your business.